Advancements in animal nutrition management enhance gut health, performance
Improve animal intestinal functionality, performance and health through research advancements in proper nutrition management.
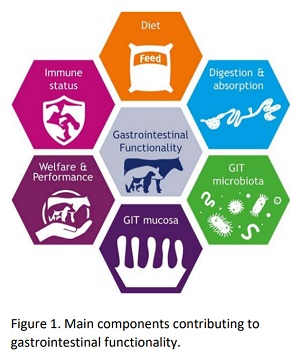
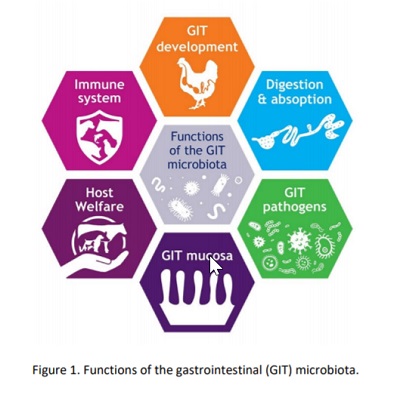
Structure of peptidoglycans and the impact on gastrointestinal tract functionality
Research elucidates meaningful relationships between the host mucosal immune system, the microbiome, and feed ingredients. Considering non‐ingredient components, the peptidoglycan (PGN) content in the GIT lumen and subsequent effects on digestibility and absorption looms into view.
Read more at wattagnet.com